MSME Policy in India: Overview, Features and Steps
India’s economic growth would be greatly enhanced by the Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs), as they constitute almost 30% of India’s GDP and provide employment to over 110 million people. These enterprises are instrumental in promoting economic self reliance, innovation and entrepreneurship. In order to enhance their contribution, government came up with the MSME policy that creates the enabling environment for business growth.
MSME policy in India includes measures to allow easy accessibility to credit; market promotion; skill development initiatives. These frameworks promote sustainable growth, technological innovation and job creations and make MSMEs globally competitive. In the last few years, MSME government policies have witnessed changes and updates to address challenges like access to market, funding gaps and regulatory burden.
Policies of MSME changes and their implications are what we will look at in this article. Business owners and their stakeholders need to understand these policies to be able to fully utilize the benefits that are available for use and to be successful in the long term in this industry.
Overview of MSME Policy in India:
The MSME policy is meant to help uplift small scale enterprises by giving a friendly business environment. MSME sector can be made up of small, hapless craft industries till high tech industries, and together contribute 48 percent of the total exports. The government has implemented many MSME policies in recognition of their significance with the following goals in mind:
- Simplifying Regulations: Reduced compliance requirements allow MSME’s to focus on growth.
- Financial Support: Operational costs for businesses are reduced by subsidized loans, credit guarantees and tax benefits.
- Technology Adoption: The policy encourages upgrading outdated practices through subsidized programs.
- Market Access: Schemes facilitate domestic and international market opportunities.
The MSME government policies have their focus not only on economic development but also on social development through employment generation in various regions across the nation. For example, funding is provided to help start new businesses through the Prime Minister’s Employment Generation Programme (PMEGP).
In addition, the MSME policy covers inclusion of groups such as women and rural entrepreneurs that are under represented. To encourage their participation, initiatives such as the Women Entrepreneur Support Scheme have been launched. These policies make sure that MSMEs stay competitive, productive and inclusive to ensure that the government continue to focus on equality in economic and sustainable development.
Key Features of MSME Policy:
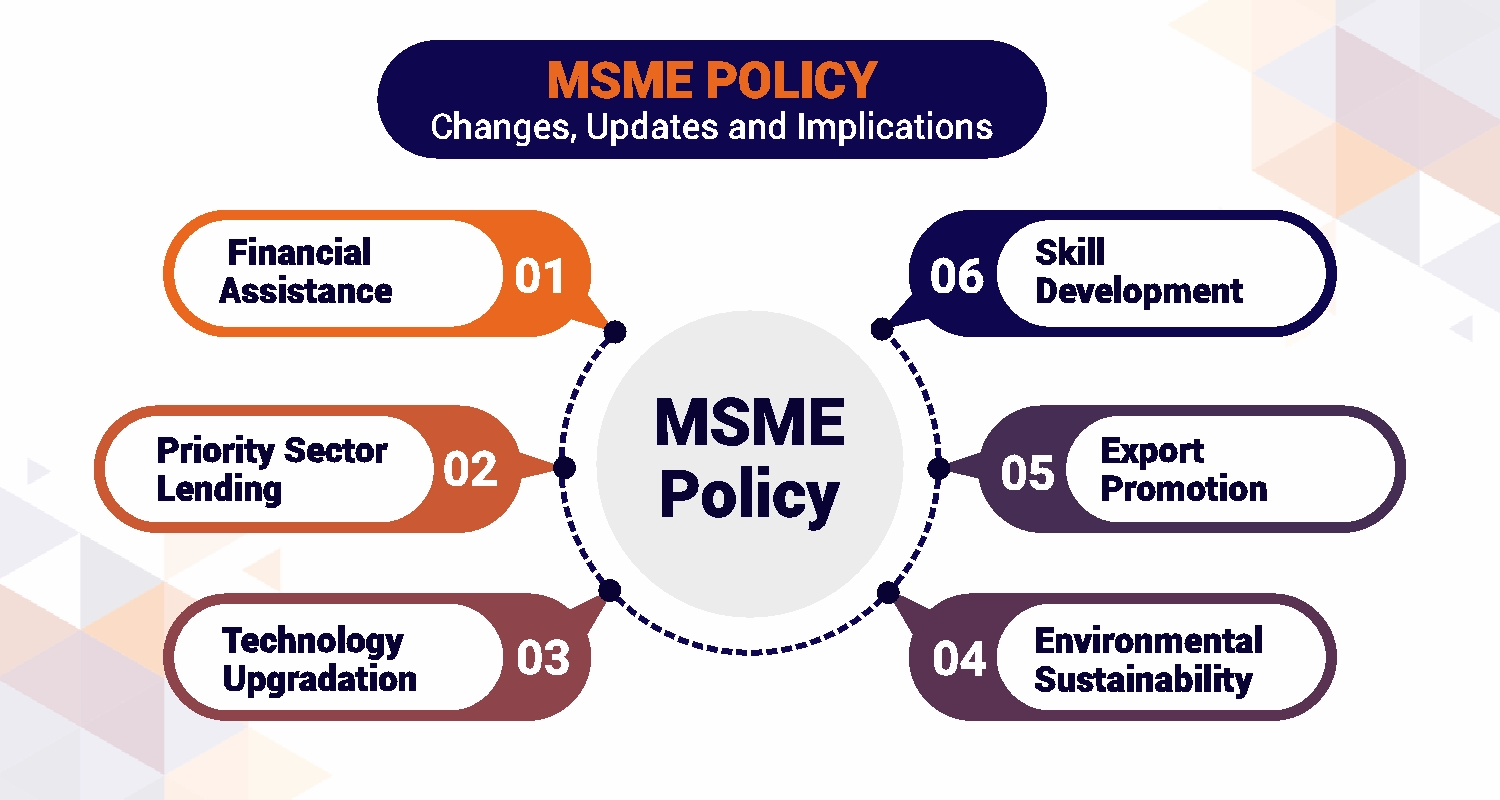
The MSME policy comprises several essential features that support businesses across various growth stages. These features include:
1. Financial Assistance
- Mudra Loans: Under Mudra Yojana, Micro enterprises can get collateral free loans at a maximum of ₹10 lakh.
- Credit Guarantee Fund Scheme (CGTMSE): It provides collateral free credit to MSMEs, that is, wider financial access.
2. Priority Sector Lending
A big chunk of the banks’ lending is required to be made to the MSME sector. This covers the provision of affordable free credit, thus alleviating the stress of finance to businesses.
3. Technology Upgradation
MSMEs under programs such as Credit Linked Capital Subsidy Scheme (CLCSS) may adopt modern technologies and enhance productivity.
4. Skill Development
The National Skill Development Corporation (NSDC) has skill development initiatives for entrepreneurs and workers to gain necessary skills to make them market relevant.
5. Export Promotion
- Subsidized certifications and export-related training programs prepare MSMEs for global markets.
- The International Cooperation Scheme, for example, enables international trade shows and buyer-seller meetings.
6. Environmental Sustainability
The “Zero Defect Zero Effect” initiative is an eco friendly manufacturing initiative, and ensures the businesses follow global environment standards.
These features have each proven to be central to enhancing the competitiveness and operational running of MSMEs. The use of these features by entrepreneurs enables them to attain sustainable growth and innovation, making it clear that MSME government policy is effective.
Recent Changes in MSME Policy:
In recent years, significant updates have been introduced to the MSME policy in India, reflecting the government’s adaptive approach to economic challenges. Key updates include:
1. Revised Definitions
Earlier, MSMEs were classified solely based on investment. The new criteria include both investment and turnover, widening the policy's coverage:
- Micro categorization: To be considered Micro, an investment must be less than ₹1 crore and turnover must be less than ₹5 crore.
- Small categorization: To be considered Small, an investment must be less than ₹10 crore and turnover must be less than ₹50 crore.
- Medium categorization: To be considered Medium, an investment must be less than ₹50 crore and turnover must be less than ₹250 crore.
2. Udyam Registration Portal
The registration process for MSMEs in this one stop digital platform has been simplified. Over 1.25 crore businesses have registered since it was launched, which means they get easier access to government benefits.
3. Emergency Credit Line Guarantee Scheme (ECLGS)
In reaction to the COVID-19 pandemic, the ECLGS was launched to provide collateral free loans of ₹4.5 lakh crore to MSMEs. The scheme helped over a dozen million businesses keep afloat during tough times.
Quick & easy loans for your business growth
Apply Now4. Export Incentives
With India aiming to double its exports by 2030, MSMEs are receiving robust support through:
- Duty-free imports for manufacturing inputs.
- Export credit at subsidized rates.
5. Technology-Driven Growth
Digital lending platforms have improved access to finance for MSMEs, while schemes like the Technology and Quality Upgradation Support drive the adoption of advanced manufacturing methods.
Case Studies:
- Export facilitation schemes helped a textile MSME based in Surat, increase its global sales by 20 per cent.
- ECLGS has given a ₹ 25 lakh loan to a rural food processing unit in Uttar Pradesh, weaving in life after the pandemic.
The updates reflect the government’s utter commitment to making MSME government policies more inclusive and in touch with growing problems. To unlock the growth opportunities, however, entrepreneurs must learn to adapt to these changes as well.
Implications of MSME Policy Updates:
MSME policy updates are important both opportunities and challenges in growth of business, which is why it is a crucial aspect. It’s important to understand these changes if you want to leverage them for business success.
Positive Impacts:
The updates in MSME policy have led to:
- Improved Financial Stability: The collateral free loans and the reduction in the overall borrowing costs are much needed liquidity for MSMEs.
- Enhanced Competitiveness: Export oriented schemes, and the provision of technology support, make it possible for businesses to exhibit competences on the global stage as competitors.
- Employment Generation: Increased access to credit facilitates MSMEs’ expansion and job creation.
Challenges:
- Awareness Gaps: It is still a mystery for many entrepreneurs to know that there are changes in MSME government policies.
- Infrastructure Deficits: Physical and digital infrastructure in rural areas are limited and impedes the policy implementation.
Future Opportunities:
The evolving MSME policy signal growth opportunities for startups, rural businesses, and women entrepreneurs. These upgrades can be made use of by MSMEs for long term success if they continue to be proactive and educated.
Role of Banks and NBFCs in Supporting MSME Policies:
Financial institutions play a big role in carrying out MSME policies. The MSME policy, aims to provide MSMEs tailored financial solutions, resources and guidance to enable growth and sustainability, and it is important for this to happen through collaboration between policymakers, banks and NBFCs.
Banks:
- Mudra and ECLGS scheme can offer low cost loans.
- Work directly with businesses to conduct workshops promoting financial literacy, in order to assist businesses better understand how to choose a loan that is rightfully authorized and documented.
NBFCs:
- Provide customized financing for rural MSMEs that lack access to traditional banking.
- Use digital platforms to streamline credit approvals.
Example:
After getting ₹15 lakh through an NBFC under the Mudra scheme, a dairy farm in Karnataka expanded its operations. This policy requires collaboration between policy makers, banks, and NBFC.
Government Initiatives Supporting MSMEs:
Different dynamic government initiatives are supporting the development of India's MSMEs. The aim is to facilitate this MSME policy with several financial assists, mentorship and skill building opportunities as part of these programs. These initiatives help address critical challenges businesses face, driving innovation, inclusivity and resilience, to build a strong foundation for economic growth and entrepreneurship. Several initiatives complement the MSME policy in India, such as:
Make in India
- In an effort to make India a worldwide manufacturing hub, the "Made in India" campaign was launched in 2014 with the intention of encouraging domestic production.
- It offers MSMEs financial incentives, simplified regulations, and access to global markets.
- Sectors like textiles, electronics, and automobiles benefit significantly, driving innovation and employment opportunities while reducing dependency on imports.
- This initiative aligns closely with the policies of MSME.
Startup India
- Startup India fosters entrepreneurship by offering seed funding, tax exemptions, and a supportive ecosystem for innovative startups, including MSMEs.
- Initiatives like the Startup India Seed Fund Scheme help businesses scale operations and develop market-ready solutions.
- Focused on technology, agriculture, and green energy, this program encourages startups to create jobs and build innovative solutions, complementing MSME policy in India.
Stand-Up India
- Stand-Up India was founded in 2016 with the goal of empowering women entrepreneurs and members of underrepresented groups.
- This program offers bank loans for the establishment of greenfield businesses in the range of ₹10 lakh to ₹1 crore.
- This initiative ensures inclusivity and strengthens underrepresented groups' participation in the MSME sector, aligning with MSME government policies to achieve social and economic equity.
Atmanirbhar Bharat
- Atmanirbhar Bharat is about encouraging domestic production and minimising reliance on imports.
- It includes financial packages for MSMEs, such as collateral-free loans and equity infusion.
- The initiative also focuses on enhancing global competitiveness through technological upgrades, export incentives, and digitalization.
- Its alignment with the policies of MSME reinforces India's vision of sustainable development.
These programs align seamlessly with the Indian MSME policies, empowering entrepreneurs through financial assistance, skill enhancement, and market access. By addressing diverse needs such as inclusivity, innovation, and self-reliance, they not only bolster entrepreneurship but also play a vital role in driving sustainable economic growth and ensuring India's competitiveness on a global scale.
Steps for MSMEs to Leverage the Policy
In order for the MSME policy to fully be realized by entrepreneurs, they have to take advantage of the implementation through government schemes, use digital tools and be in the know of policy changes. MSMEs are made to take these proactive steps to ensure that they can utilize and maximize on existing resources, and access to financial benefits and opportunities for growth in a fast changing market. Following are the steps:
Step 1: Register on Udyam Portal
- The first and, most important, step for MSMEs who would want to receive government support, is to register on the Udyam Portal.
- Businesses get various credit guarantee, subsidies and priority sector laying options when they register.
- This simple registration process opens doors to numerous benefits, making it essential for every MSME.
Step 2: Utilize Digital Platforms
- MSMEs are given a chance to link up with government buyers directly, digital platforms like Government e-Marketplace (GeM) provide.
- Through GeM, MSMEs can access government procurement opportunities, increase transparency and increase business opportunities.
- This digital shift reduces barriers, enabling MSMEs to compete in a larger, national marketplace.
Step 3: Stay Informed
- MSME government policies are continuously changing and keeping entrepreneurs up to date with the latest MSME government policies will ensure that entrepreneurs can remain compliant with new regulations and avail the latest incentives.
- MSME’s can take advantage of such opportunity by getting in touch with industry bodies, subscribing to the newsletters and participate in policy discussions to be aware of government initiatives and reap all the opportunity available.
It makes sense for MSMEs to be proactive in helping them pass through the labyrinth of policy updates. A business can adapt to new regulations, take advantage of new opportunities and keep sustainable in an ever more competitive environment by taking timely action, such as registering for schemes, staying aware of the changes in the policy, and the use of the available digital tools at the time.
Conclusion
MSME policies are instrumental in achieving economic self reliance and the global competitiveness. The government has also enhanced the access of businesses to credit, technological support and export incentives with recent updates. Entrepreneurs can open up new growth opportunities by learning and harnessing MSMEs policies that help India’s dream of inclusive and sustainable development.
FAQs on MSME Policy
1. What is the MSME policy in India, and why is it important?
Ans. Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises supported through several financial and non financial benefits as contained in the MSME policies. These MSME policy help these entrepreneurs get the credit, subsidies and the skill development opportunities to create jobs and spur economic growths empowered businesses with easier access to credit, technological support, and export incentives. By understanding and leveraging MSME policies, entrepreneurs can explore new growth opportunities, contributing to India’s vision of inclusive and sustainable development.
2. How can MSMEs benefit from the MSME policy?
Ans. MSME policy, for instance, can drastically help MSMEs, including access to financial help, tax inducements, priority sector financing. These policies are meant to make MSME more competitive so that they can expand, improve their technology, to promote productivity. These policies of MSME helps businesses stay updated with new opportunities and financial schemes.
3. What are some of the key features of MSME policy in India?
Ans. Some essential features in MSME policy in India such as financial support, skill development and priority sector lending. These MSME policies are technology upgradation oriented as well as with easy access to loans to promote growth priority sector lending. With a focus on technology upgradation and easy access to loans, these MSME policies are designed to boost growth. Entrepreneurs can then dig in to financial and developmental opportunities by going down the MSME policies.
4. How can MSMEs stay updated with MSME policy?
Ans. To keep up with MSME policy, business can get in touch with industry bodies, and workshops, and government portals can be monitored. MSMEs ensure that they comply with these initiatives as well as can make full benefits from the latest changes in the MSME policy in India. The need for a proactive business growth is vital for sustainability.
Quick & easy loans for your business growth
Apply NowDisclaimer: The information contained in this post is for general information purposes only. IIFL Finance Limited (including its associates and affiliates) ("the Company") assumes no liability or responsibility for any errors or omissions in the contents of this post and under no circumstances shall the Company be liable for any damage, loss, injury or disappointment etc. suffered by any reader. All information in this post is provided "as is", with no guarantee of completeness, accuracy, timeliness or of the results etc. obtained from the use of this information, and without warranty of any kind, express or implied, including, but not limited to warranties of performance, merchantability and fitness for a particular purpose. Given the changing nature of laws, rules and regulations, there may be delays, omissions or inaccuracies in the information contained in this post. The information on this post is provided with the understanding that the Company is not herein engaged in rendering legal, accounting, tax, or other professional advice and services. As such, it should not be used as a substitute for consultation with professional accounting, tax, legal or other competent advisers. This post may contain views and opinions which are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the official policy or position of any other agency or organization. This post may also contain links to external websites that are not provided or maintained by or in any way affiliated with the Company and the Company does not guarantee the accuracy, relevance, timeliness, or completeness of any information on these external websites. Any/ all (Gold/ Personal/ Business) loan product specifications and information that maybe stated in this post are subject to change from time to time, readers are advised to reach out to the Company for current specifications of the said (Gold/ Personal/ Business) loan.